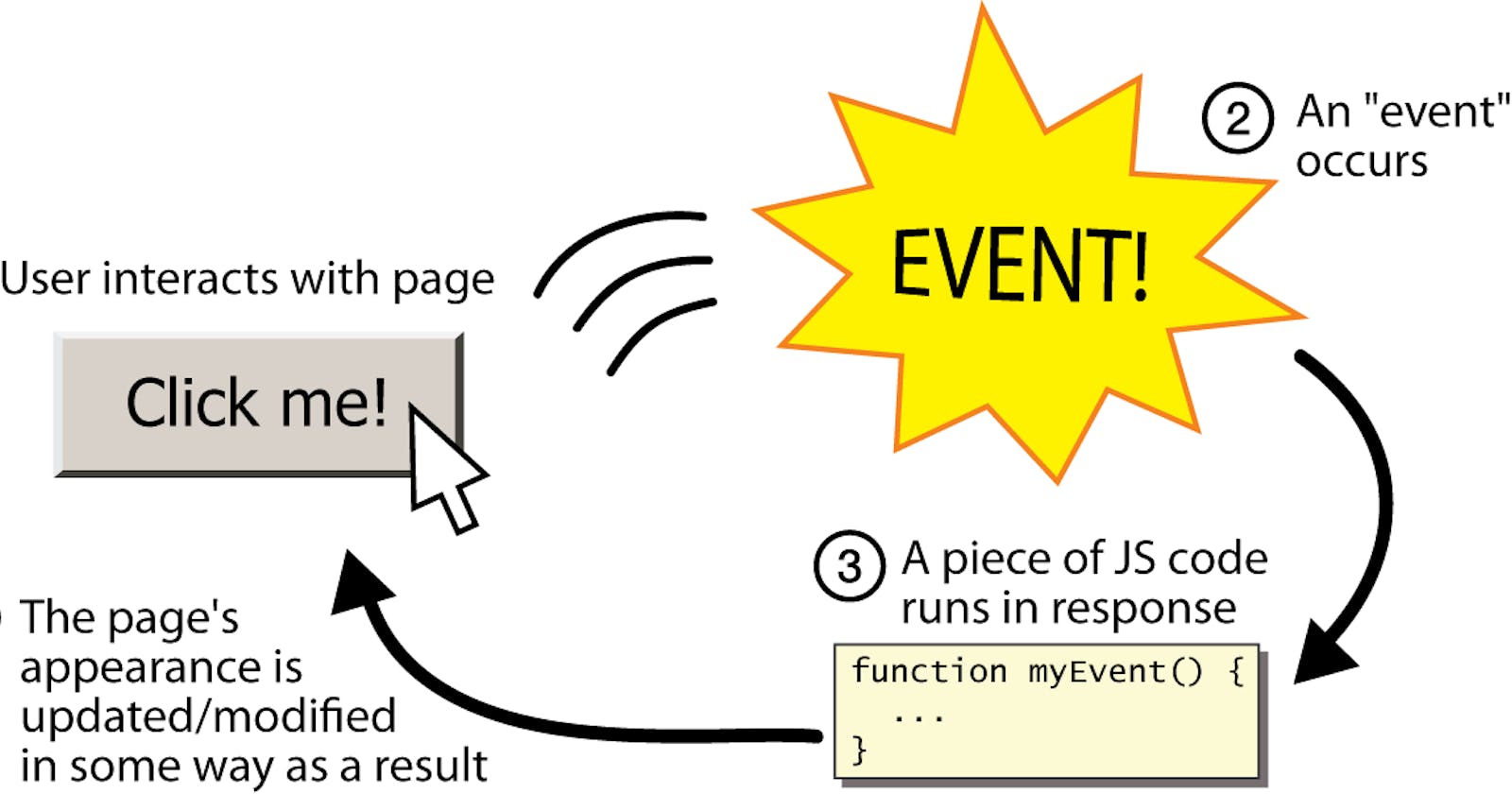
Introduction
JavaScript events are actions that the user performs on the webpage which when happens, a certain code will execute which is linked to that action. The event may be anything from mouse clicking, mouse moving, scroll, load, unload etc. There are various events in JavaScript that we will know further.
The most common browser events that in JavaScript are "click", "mouseover", "mouseout" and "keypress". The "click" event is triggered when the user clicks on an element, while the "keypress" event is triggered when the user presses a key on the keyboard. Other common events include "load", "unload" and "scroll" etc.
We can also create our own custom events using the "trigger()" method. It is very useful for performing desired tasks.
Some commonly used events of JavaScript
click Event
The click event as the name suggests related to the mouse click event. This event may be a button, a link or any other element. Click events are usually used to perform any action which are desired to be done whenever user click on the element.
To add a click event to an element, we first need to select it using DOM manipulation method in JavaScript. For example, if we wanted to add a click event to a button and log "Button Clicked" whenever we click using mouse on that button having id = "btn", we would use the following code:
Syntax
let btnEl = document.getElementById("btn");
btnEl.addEventListener("click",()=>{
console.log("Button Clicked");
});
In the above code we have selected the button by using document. getElementById method and then apply event handler which is done by .addEventListener method. The addEventListener method consists of two arguments within parenthesis. The first argument consists of the name of the event ("click")we want to apply and a function is passed as the second argument which is to be executed when the event happens.
The other events can also be written similar to the above syntax as shown above.
If we click various time on that button, lets say if we clicked on the button for 5 times then the output result in the console will be-
Output-

mouseover Event
The mouseover event is the event which occurs when the mouse cursor goes over the element.
Syntax
let btnEl = document.getElementById("btn");
btnEl.addEventListener("mouseover",()=>{
console.log("Mouse is on Button");
});
Similar to the click event we have selected the button by using document. getElementById method and then apply event handler which is done by .addEventListener method. The addEventListener method consists of two arguments within parenthesis. The first argument consists of the name of the event we want to apply ("mouseover") and a function is passed as the second argument which is to be executed when the event happens.
If we take mouse over that button then the output will be-
Output-

mouseout Event
The mouseout event is the event which occurs when the mouse cursor goes outside the element.
Syntax-
let btnEl = document.getElementById("btn");
btnEl.addEventListener("mouseout",()=>{
console.log("Mouse Out");
});
Similar to the above events we have selected the button by using document. getElementById method and then apply event handler which is done by .addEventListener method. The addEventListener method consists of two arguments within parenthesis. The first argument consists of the name of the event we want to apply ("mouseout") and a function is passed as the second argument which is to be executed when the event happens.
If we take mouse over that button nothing happens but when we move the mouse pointer out of the button then "Mouse Out" will be logged in the console.
Output-

keypress Event
The keypress event is the event which occurs when any key of the keyboard is pressed.
Syntax-
let btnEl = document.getElementById("btn");
btnEl.addEventListener("keypress",()=>{
console.log("Key pressed");
});
Similar to the above events we have selected the button by using document. getElementById method and then apply event handler which is done by .addEventListener method. The addEventListener method consists of two arguments within parenthesis. The first argument consists of the name of the event we want to apply ("keypress") and a function is passed as the second argument which is to be executed when the event happens.
If we press any key on the keyboard within the element then it will log "Key pressed" in the console.
Output-

focus Event
The focus event fires when the element gets focus.
Syntax-
let btnEl = document.getElementById("btn");
btnEl.addEventListener("focus",()=>{
console.log("Focused on button");
});
Similar to the above events we have selected the button by using document. getElementById method and then apply event handler which is done by .addEventListener method. The addEventListener method consists of two arguments within parenthesis. The first argument consists of the name of the event we want to apply ("focus") and a function is passed as the second argument which is to be executed when the event happens.
If we click outside the element then the focus event is not fired and nothing happens. But afterwards when we click on the element (button) it becomes in the focus state and the event fires which executes the funciton which is passed as the second argument and logs "Focused on button" in the console.
Output-

blur Event
The blur event is exactly opposite of the focus event as described above. It fires when the element lost focus.
Syntax-
let btnEl = document.getElementById("btn");
btnEl.addEventListener("blur",()=>{
console.log("Focus lost");
});
Similar to the above events we have selected the button by using document. getElementById method and then apply event handler which is done by .addEventListener method. The addEventListener method consists of two arguments within parenthesis. The first argument consists of the name of the event we want to apply ("blur") and a function is passed as the second argument which is to be executed when the event happens.
If we click within the element then the blur event is not fired and nothing happens. But afterwards when we click outside the element (button) it lost focus and the event fires which executes the function which is passed as the second argument and logs "Focus lost" in the console.
Output-

Conclusion-
All events are not covered within this blog post. There are various other events like load, unload, mousedown, mouseup, abort, keydown, keyup, load, loadeddata, mousemove, pause, paste, play etc, which are very useful make things interactive. JavaScript events plays an important part in it. They can be used to perform an action, such as opening a new page or submitting a form.